Retrocalcaneal bursitis and Achilles tendon tendinosis
First published on SonoWorld
Case Presentation
30 year old athlete with persistent heel pain on the right side


Final Diagnosis
Retrocalcaneal bursitis and Achilles tendon tendinosis
Discussion
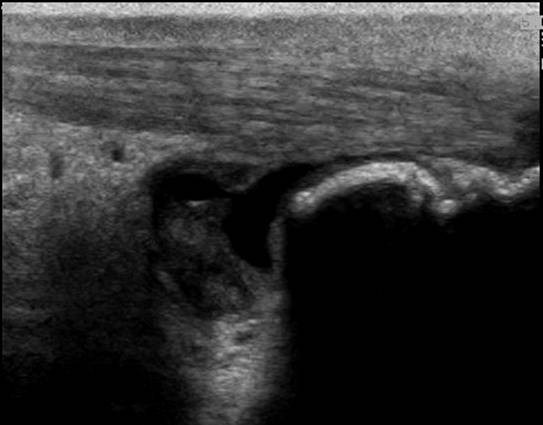
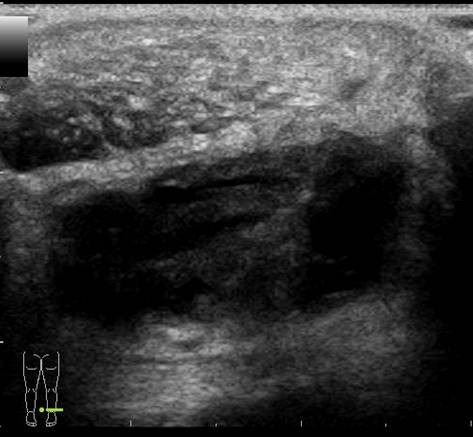
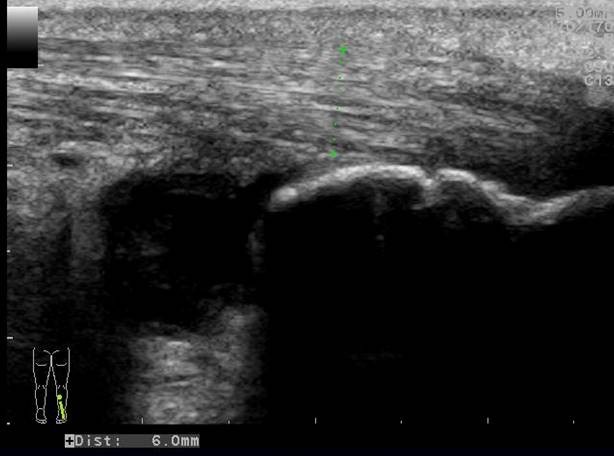
There is a thick walled fluid filled bursa between the Achilles tendon and the calcaneal bone. The color Doppler images show hypervascularity of the bursal wall.
A minimal amount of fluid in the retrocalcaneal bursa can often be found.
A retrocalcaneal bursitis is caused by friction of the Achilles tendon over the upper part of the calcaneal bone. It is often an overuse injury found in athletes.
Signs indicating a bursitis are
A rounded contour
A thick wall
Hypervascularity
Increased echogenicity of Kagers fat
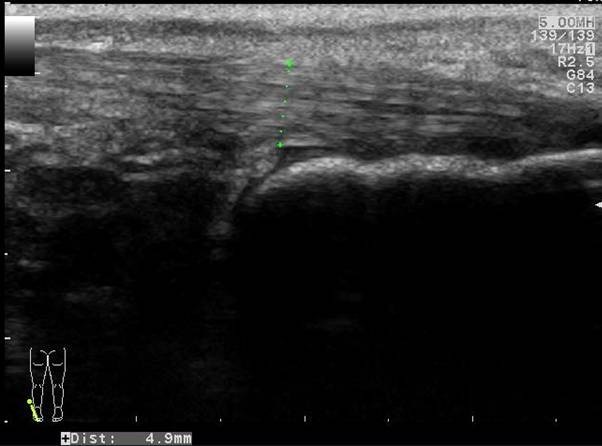
A retrocalcaneal bursitis is often found in combination with a tendinosis or tendinopathy of the distal Achilles tendon. Common signs of an Achilles tendinosis or tendinopathy are
Swelling of the tendon
Inhomogenous hypoechoic aspect
Loss of the normal fibrillar pattern
Hypervascularity or neovascularity
In this case there is only slight swelling of the tendon and the normal fibrillar pattern is preserved. There is however a marked hypervascularity.
For more cases of retrocalcaneal bursitis or Achilles tendon pathology visit www.ultrasoundcases.info
Follow Up
Treatment of a retrocalcaneal bursitis is usually conservative with cessation of the sports activities. An ultrasound guided puncture of the bursa and injection of a combination of a corticosteroid and an analgesic can quickly relieve the patient pain
Schepsis AA, Jones H, Haas AL.Achilles tendon disorders in athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2002 Mar-Apr;30(2):287-305.