Perforated emphysematous cholecystitis with abscess in the omental bursa
First published on SonoWorld
Case Presentation
80 year old male patient with severe pain in the right upper abdomen and fever. The patients medical history is unremarkable without previous surgery or an ERCP.
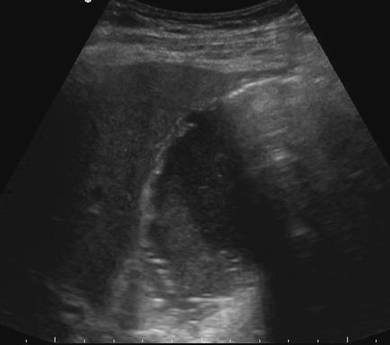
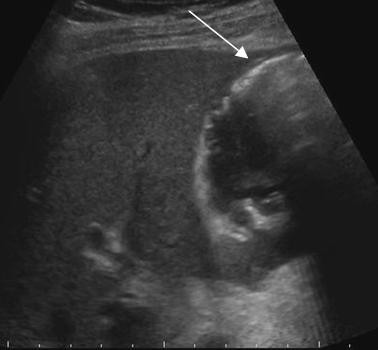
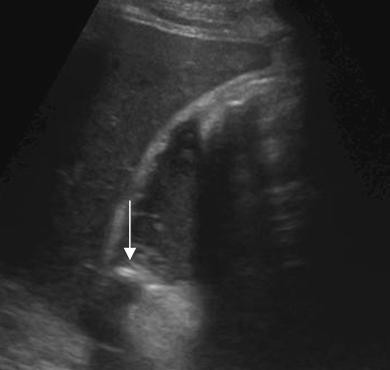
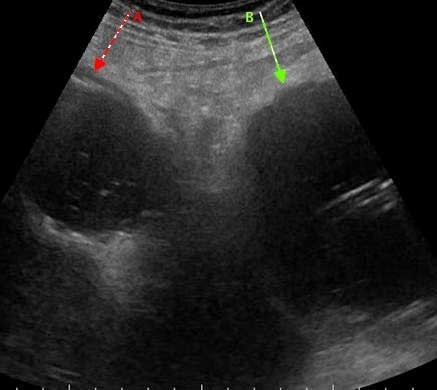
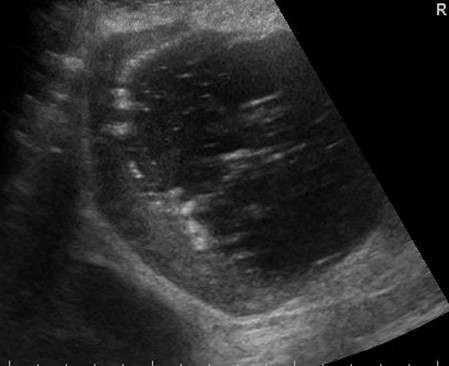
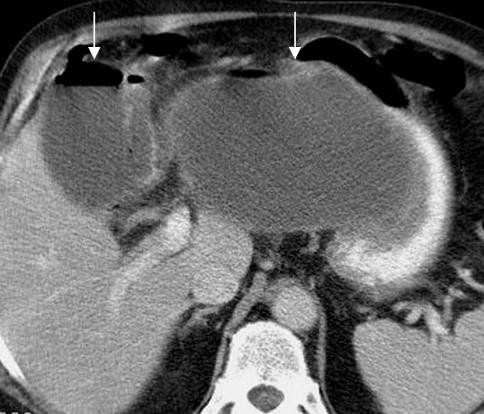
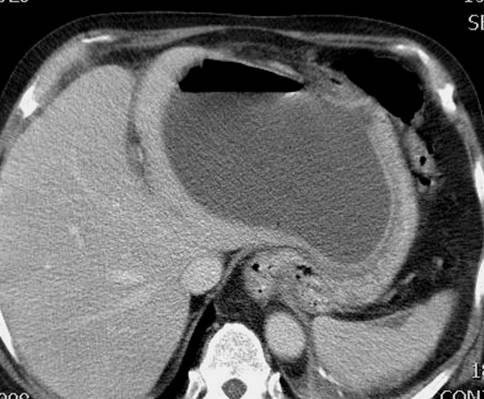
Differential Diagnosis
Air in the gallbladder and biliary tract can be caused by an abnormal communication between the digestive tract and the biliary tree. Possible causes are
- a previous papillotomy
- previous surgery such as a choledochoduodenostomy
- perforation (often a gallstone) to the digestive tract
The other cause of air in the gallbladder and sometimes in the biliary ducts, is an emphysematous cholecystitis. In most cases of an empysematous cholecystitis however there is no air in the bile ducts, because the cystic duct is often obstructed. This makes a differentiation possible
In this case there is an emphysematous cholecystitis
Final Diagnosis
Perforated emphysematous cholecystitis with abscess in the omental bursa
Discussion
Emphysematous cholecystitis is an acute infection of the gallbladder caused by gas-forming organisms
Several factors can account for an emphysematous cholecystitis
Gallstones
In most of the patients with an emphysematous cholecystitis gallstones are found, often with obstruction of the cystic duct. However an emphysematous cholecystitis can also be found in cases of an acalculous cholecystitis
Vascular compromise
An emphysematous cholecystitis is more common in elderly patients with atherosclerosis. Diabetes is not uncommon. Although gallstones are more common in females, an emphysematous cholecystitis is more frequently found in males
Infection with gas-forming organisms
In about 1/3 of the cases clostridium perfringens is found. Other organisms are E. Coli and Klelbsiella
The mortality rate of an emphysematous cholecystitis is much higher than in cases of a non emphysematous cholecystitis.
Because of gallbladder wall ischemia there is a high risk of perforation of the wall. In this case an abscess has formed in the omental bursa.
The ultrasound findings of an emphysematous cholecystitis are.
Highly reflective air in the wall or the lumen of the gallbladder
Air in the wall must be differentiated from calcium which can be found in a porcelain gallbladder. If in doubt X ray can help differentiating between the two
An ill defined wall is not uncommon.
Thickened bile and or stones are a frequent findings
For more examples of an emphysematous cholecystitis visit www.ultrasoundcases.info
Follow Up
Surgery in a case of an emphysematous cholecystitis has a very high complication rate. A percutaneous drainage procedure under ultrasound guidance was performed of both the gallbladder and the abscess.
The patient recovered quickly and an ultrasound examination performed a few weeks later showed complete disappearance of the abscess and a small shrunken gallbladder
Konno K, Ishida H, Naganuma H, Sato M, Komatsuda T, Sato A, Ishida J, Sakai T,Watanabe S. Emphysematous cholecystitis sonographic findings. Abdom Imaging 2002 Mar-Apr;27(2):191-5.
Gill KS, Chapman AH, Weaton MJ The changing face of emphysematous cholecystitis Br. J Radiol. 1997 Oct;70(838):986-91.
Alan A Bloom, Prospere Remy Emphysematous Cholecystitis Emedicine