5. Color Doppler imaging of the carotid arteries
5.1 How is color Doppler applied in carotid ultrasound?
Doppler ultrasound is a modality, which allows us to study blood flow in the vessels during carotid ultrasound. It is performed as part of a standard carotid ultrasound exam. Both spectral and color Doppler provide information on blood flow velocity and the direction of flow. Doppler information must always be combined and interpreted together with the B mode image.
5.2 How is Doppler used in a transverse view?
The transverse view does not allow us to determine the direction of flow. Therefore PW Doppler is rarely used in a transverse view (we can not correct the Doppler angle). However, there are several ways how color Doppler can be applied:
| Color Doppler in a transverse view |
|---|
| Can be used to spot turbulences |
| To see if the entire vessels fills (excluding or detecting soft plaque) |
| Can help to discern arteries from veins |
| Can help to discern internal from external carotid artery |
| Can help to follow vessels during a sweep |
| Can help to detect tortuous vessels |
| Use a rectangular color box |
| Angulate transducer caudally or cranially to get a suitable Doppler angle (avoid a mixed red and blue signal) |
| Adjust PRF |
| Also try Power Doppler |
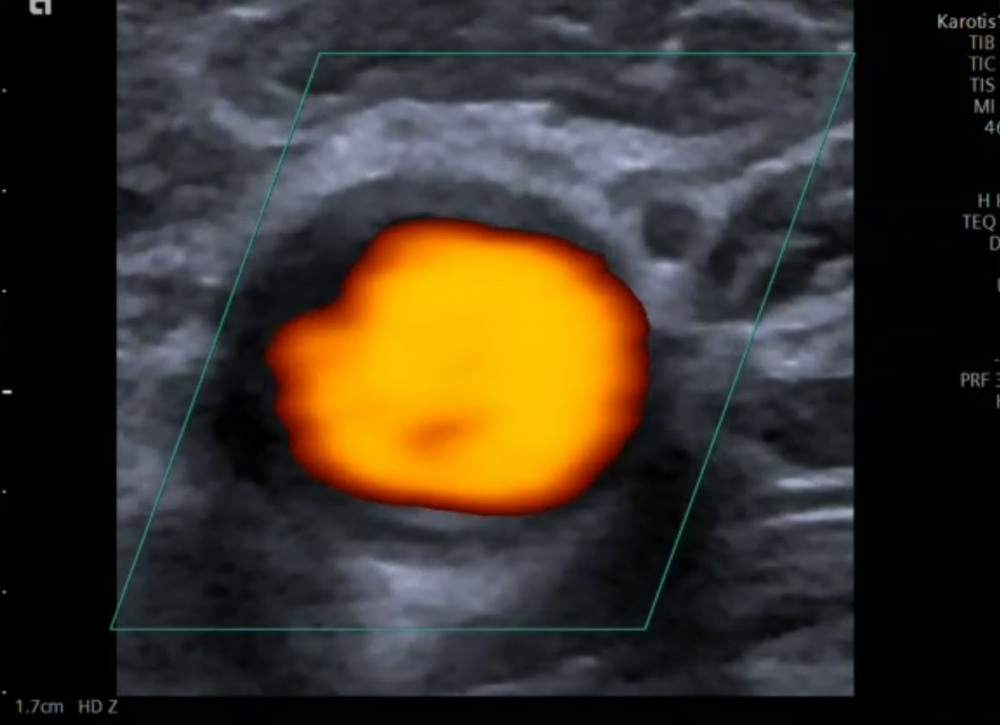
5.3 What is Power Doppler and how is it used in carotid ultrasound?
Power Doppler is an ultrasound modality, which uses only the amplitude of the Doppler signal to display flow. The Doppler intensity is displayed in colors from red (low intensity) to yellow (high intensity). Power Doppler is angle independent and is not affected by aliasing. In contrast to color Doppler Power Doppler does not display the direction of flow. In general it is more sensitive for lower flow velocities and flow in small vessels. Power Doppler can also be used to examine vessels in superficial organs such as the thyroid or testicles and to visualize vessels in tumors.
| Power Doppler |
|---|
| Power Doppler uses the amplitude of the Doppler signal to display flow |
| More sensitive for the detection of blood flow than color Doppler |
| We loose the information of blood flow direction |
| There is no aliasing |
| It is less angle dependant |
| Allows visualization of small vessels |
| It can be used to visualize the inner contour of the vessels and to detect or exclude areas of narrowing |
5.4 How is Doppler used in a longitudinal view?
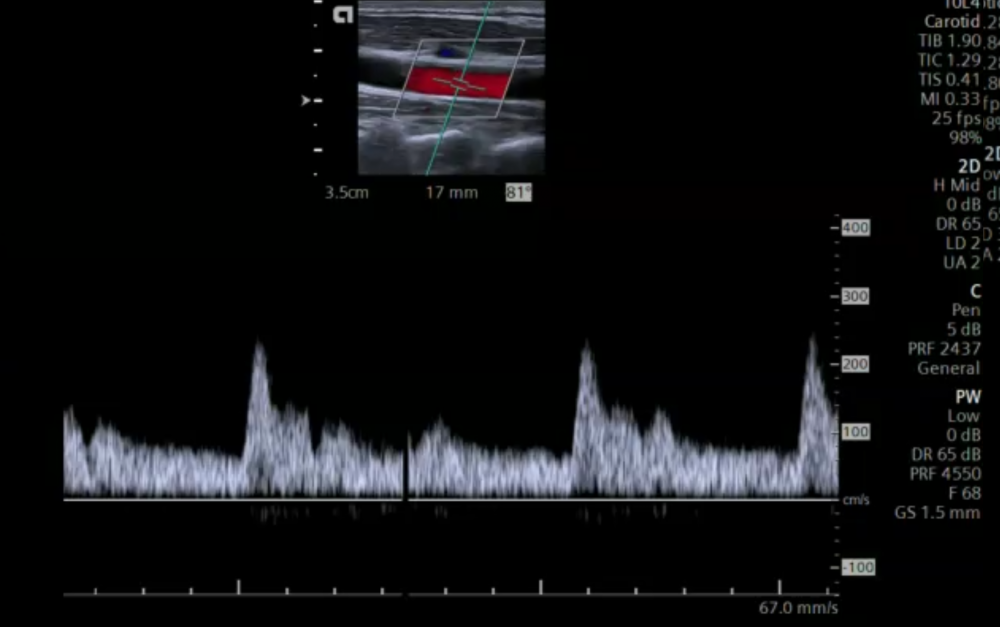
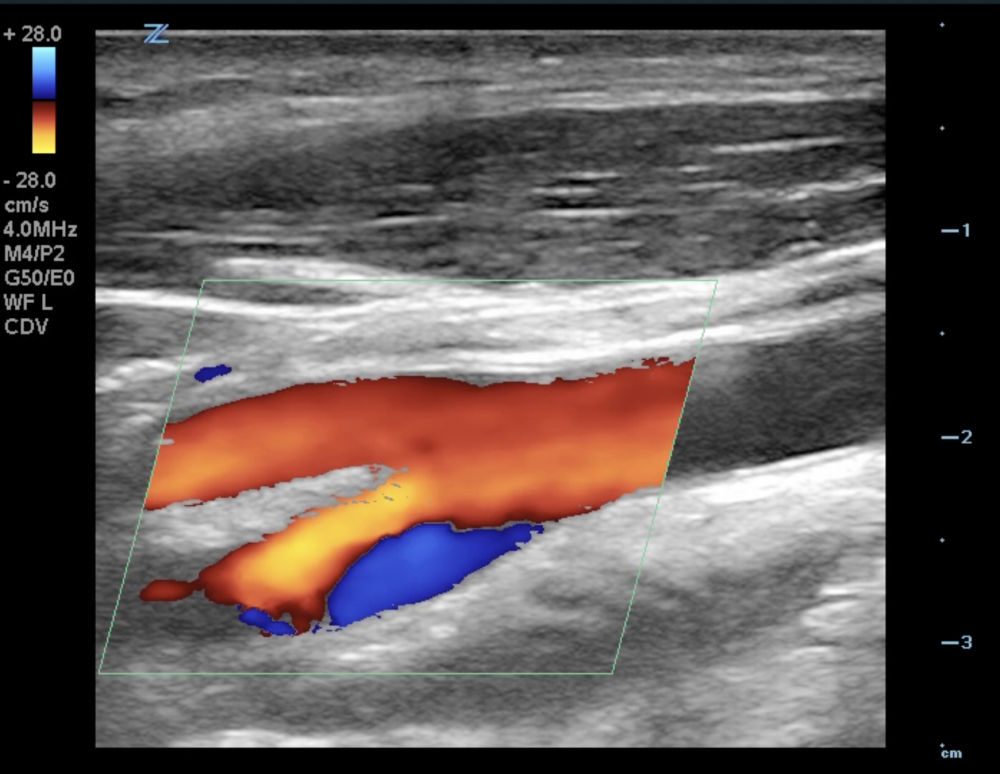
Color Doppler is used to demonstrate the direction of flow and to depict areas of higher flow velocities. Higher flow velocities are characterized by aliasing. Color Doppler (together with power Doppler) is also helpful to depict plaques with low echogenicity (soft plaque), which might be missed with B mode imaging alone. Spectral Doppler allows characterization of the vessel (i.e. vein vs. artery, internal vs. external carotid artery) and measure flow velocities (systolic and diastolic), which are then also used to calculate indices. Flow velocities allow us to quantify the degree of a stenotic lesion and to determine if such a lesion is relevant or not.
5.5 What is the color Doppler Box and how should it be adjusted during carotid ultrasound?
The color box is the region of interest in which color flow information is displayed. The size, position and angle of the color box can be adjusted.
| Color Box |
|---|
| The color box is the region of interest where color flow will be depicted |
| The scale will tell you what the PRF (aliasing limit) and the direction of flow is (you can invert the color scale) |
| Tilt the transducer (caudal and cranial) to optimize your angle of insonation (Try not to be parallel to the vessel with your imaging orientation - as in A) |
| The color box angle can be adjusted so that you are at an optimal angle to blood flow |
| The diagonal (long axis) of the box should be as parallel as possible to the vessel wall |
| No angle correction is required if flow is directly towards or away from the transducer (parallel to flow) |
| If the color box is optimized your color signal will be much better |
The orientation of the color box should follow the direction of flow. If the Doppler interrogation is perpendicular Doppler does not allow us to determine the direction of flow. This means you will get a mixed red / blue signal. Try to use a flow orientation where the Doppler angle is as parallel to blood flow as possible. This can be achieved by changing the angle of insonation and by adjusting the color box. The long axis of the box should approximate the direction of flow

5.6 How should color Doppler be adjusted?
It is important not only to adjust the size and angle of the color box, but also to adjust the color gain, set the aliasing velocity (PRF) and to chose an appropriate color map. Here are some important tips:
| Color Doppler tips |
|---|
| First optimize your PRF (CCA). Choose a velocity which is just below the Nyquist limit (aliasing) |
| Primarily use conventional Doppler, add Power Doppler in specific situation |
| Always use the same maps (chose one that fits you), Optimize you color Box |
| Optimize colors gain (avoid high gain settings, which cause blooming artifacts) |
| Observe the direction of flow |

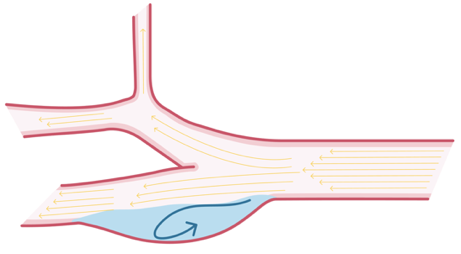
5.7 What is recirculation in carotid ultrasound?
| Recirculation |
|---|
| Recirculation which is also called „flow separation“ is a specific flow pattern found in the bulb |
| Lower peak systolic velocity flow |
| Circulating and retrograde flow |
| The magnitude varies from patient to another |
| It has been hypothesized that the flow dynamics of the bulb play a role in the likelihood for developing plane and stenosis |
| The presence of recirculation can help to identify the region of the bulb |
If you like the way we teach, please leave a message!